BIOTA West GIS training workshop in Cotonou (Benin) from 25.02- 28.02.2008
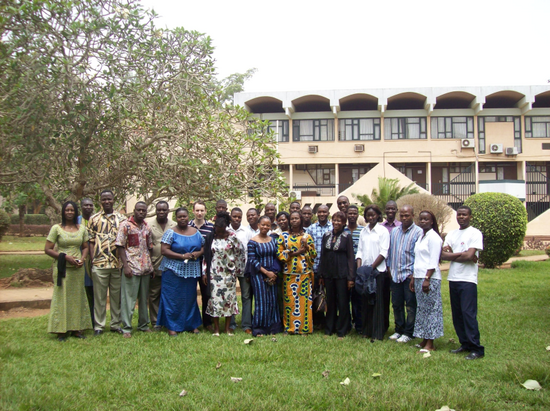

The BIOTA West Remote Sensing Group facilitated a one week GIS training workshop in Benin during February 2008 for 25 BIOTA West PhD students from Benin, Burkina Faso and the Ivory Coast.
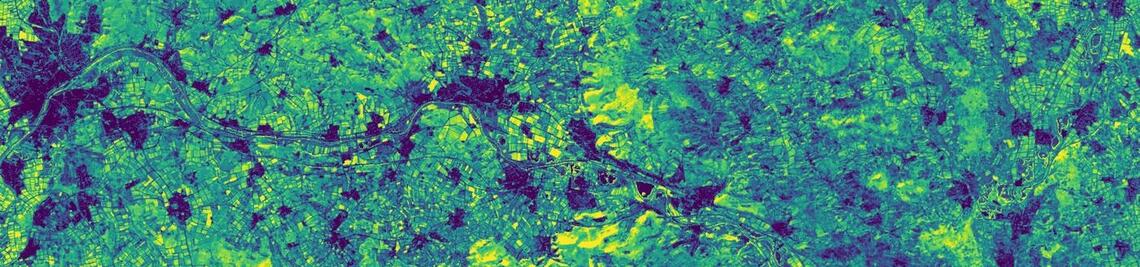
As poverty is a potential threat to biodiversity, formation of capacities at different levels and knowledge sharing with all involved stakeholders is a key concern of BIOTA WEST. Thus BIOTA is not just a research project; it is also a project in which capacity building is an important and key component. Within this framework, the Remote Sensing Unit of the University of Wuerzburg, facilitated a Geographical Information System (GIS) and remote sensing training workshop in Cotonou (Benin) from the 24th of February to the 28th of February 2008. The foremost purpose of the training was to familiarize the BIOTA West PhD students, as well as other BIOTA junior scientists, with basic methods of GIS data integration, manipulation and finally map production methods, also aligned to biodiversity related GIS data query needs in West Africa. The participants worked with the ArcGIS software and learned to integrate GPS field data with the GIS spatial layers that is the visualization of GPS points through a map. Further the participants learnt how to acquire satellite data from the internet, the processing of the imagery and how to perform a simple image analysis using the software ERDAS IMAGINE.

Outline of the Course
Part 1: Remote sensing and his application
- Introduction to remote sensing
- How to get information on an object on the surface of the earth?
- What are the different areas of applications of remote sensing?
Part 2: Overview of satellite imagery/products, primarily used within BIOTA
- Products and availability
Part 3: Utility and constraints of satellite data sets for key hydrology applications
- Landsat/SPOT/ASTER
- Processing data
Part 4 (theory): Demonstrate utilities for hydrological and biodiversity applications
- Deflection of flooding levels and thus thematic wetland gauge values
- How to map wetlands?
- Utility of the wetland data
- Simple land cover mapping
Part 5: Data acquisition and distribution
- MODIS data
- Landsat, DMSP, other data
Part 6 (practical work): Demonstrate utilities for hydrological applications
- Working with continuous data
- Working with thematic data
- Modis wetland
Part 7: Introduction to Erdas Imagine software
Part 8: GIS
- Introduction to GIS
- GPS sampling points
- Create a map
Teaching material is available on request.