Detailed Information for the M.Sc. GEOSPHERES
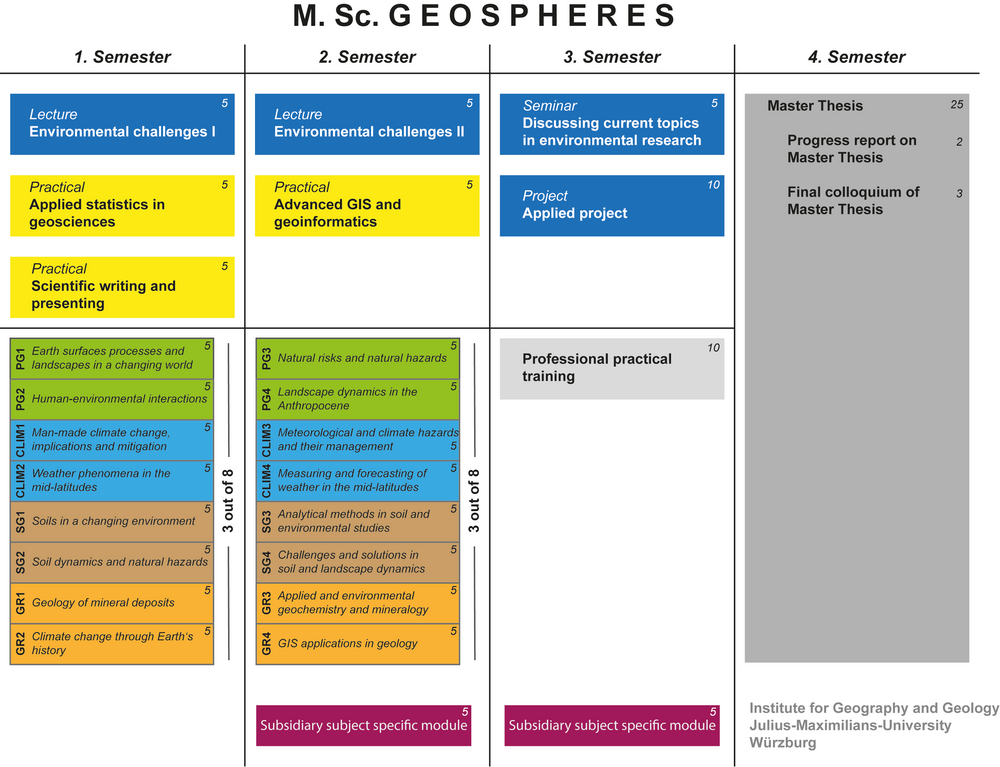
Mandatory Courses
Mandatory courses are attended by all students. They provide an overview of the different topics covered by the the GEOSPHERES master program.
Environmental challenges I
Environmental challenges II
Discussing current topics in environmental research
Applied project
Methods
In the methods section you will aquire advanced methods for interpreting geospatial data, gaining the skills to analyze complex spatial patterns and derive meaningful insights from geographic information.
Applied statistics in geosciences
Scientific writing and presenting
Advanced GIS & geoinformatics
Elective Modules
The elective module area allows students to choose from a range of specialized courses, enabling them to tailor their studies according to their individual interests.
You have to choose 3 out of 8 courses in your first and another set of 3 in your second semester.
Each course carries 5 ECTS credits.
Focus area Geomorphology
Earth surface processes and landforms in a changing world
Human-environmental interactions
Natural risks and hazards
Landscape dynamics in the Anthropocene
Focus area Climate
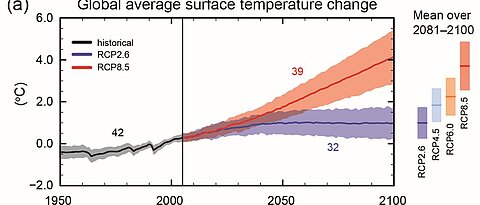
Man-made climate change, implications and mitigation
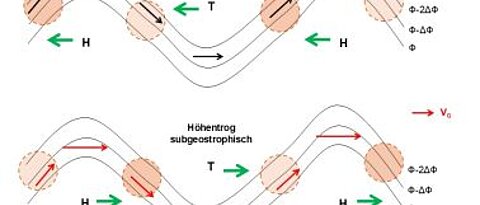
Weather phenomena in the mid-latitudes
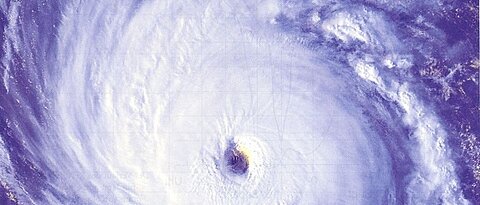
Meteorological and climate hazards and their management
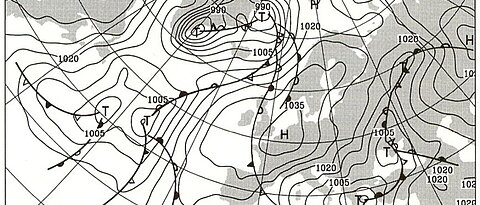
Measuring and forecasting of weather in the mid-latitudes
Focus area Soil Science
Soils in a changing environment
Soil dynamics and natural hazards
Analytical methods in soil and environmental studies
Challenges and solutions in soil and landscape dynamics
Focus area Geology
Geology of mineral deposits
Climate change through Earth’s history
Applied environmental geochemistry and mineralogy
GIS applications in geology
Work placement / Professional practical training for Students of GEOSPHERES
Students gain practical experience outside the university context. On the basis of practical experience, they develop individual qualification profiles and specific career prospects.
[3. Semester, 8 weeks, 10 ECTS]
Subsidiary subject-specific development
Courses that lead to an additional subject-relevant profile for the degree programme in the Master GEOSPHERES.
You have to choose two. Selections can be made from a large variety of courses offered by the Insitute of Geography and Geology and the JMU Würzburg.
[5 ECTS each]
MASTER THESIS GEOSPHERES
Independent processing of a scientific question and preparation of a Master's thesis (around 80 pages) [25 ECTS].
Besides the Master thesis, you have to give a progress report [2 ECTS] on your thesis and defend your thesis in a scientific debate [3 ECTS].

![[Translate to Englisch:] Studium](/fileadmin/_processed_/0/6/csm_header_studium_2df042456b.jpg)